Content
- 1 The role of calcium in the human body
- 2 Useful properties of calcium
- 2.1 Strong bones and osteoporosis prevention
- 2.2 Reduces the risk of kidney stones
- 2.3 Reduces PMS symptoms
- 2.4 Regulates blood pressure
- 2.5 Reduces the risk of cancer
- 2.6 Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
- 2.7 Helps to lose weight
- 2.8 Protects teeth
- 2.9 Normalizes acid-base balance
- 2.10 Reduces the risk of developing chronic diseases
- 3 Why calcium is useful for children and pregnant women
- 4 Daily intake
- 5 Signs of a lack of calcium in the body
- 6 Symptoms of an excess of calcium in the body
- 7 Pharmacy preparations containing calcium
- 8 Calcium foods
- 9 Calcium harm to the body
- 10 Calcium Compatibility with Other Substances
- 11 Conclusion
Of all the chemical elements present in the human body, calcium (Ca) is in fifth place in terms of percentage. The element of the table created by Mendeleev makes up 1.5% of the total body weight. The benefits and harms of calcium indicate the need for adequate intake of the nutrient.

The role of calcium in the human body
Calcium is in group 2 of the periodic table and has number 20. A substance in nature can be found only in a bound form due to the property that causes high chemical activity.
The human body includes calcium in the form of compounds:
- apatite;
- carbonates.
The mass of the mineral is up to 1.5 kg. Of this mass, 99% are teeth and skeleton. A small amount of the substance can be found in tissues, blood and intercellular fluid.
The benefits of calcium lie in its properties. The mineral is directly involved in the construction of various tissues and regulates metabolism, heart function. It is known that the element is necessary for nourishing the nervous tissue and conducting impulses. A useful mineral, due to its properties, reduces the concentration of cholesterol, stabilizes blood pressure, and helps transport important nutrients through cell membranes.
In blood plasma, calcium exists in 3 forms:
- Active ionized (60%). Calcium is involved in hormone production, transmission of nerve impulses, cell division and muscle contraction. These processes are vital.
- Non-ionized or bound... These are compounds (30%) with the substance albumin, as well as low molecular weight anions, which is 10%. The forms do not take an active part in important biochemical processes.
The mineral maintains a constant blood pH (buffer system). Together with magnesium and potassium, the effects of harmful acid-forming foods are neutralized. The amount of these elements is regulated by metabolic processes.

The benefits of calcium for the human body are undeniable. The mineral is essential for pregnant women. Adequate calcium intake ensures the development of the fetus and the well-being of the woman.
This causes significant harm to a woman's health.
Useful properties of calcium
Calcium can be both beneficial and harmful to the body, due to its properties. Experts call the following beneficial properties of the mineral:
- Bone formation. The element ensures the health and growth of hair, teeth, nails.The substance also helps to strengthen cell membranes.
- Participation in contractile activity of skeletal and smooth muscles. Thanks to the beneficial mineral, myocardial contractions, vascular walls become rhythmic.
- Stabilization of the work of the heart muscle. Calcium has the ability to reduce pressure, reduce vascular permeability. These processes take place with the direct participation of potassium, sodium and magnesium.
- Normalization of metabolic processes, increased permeability of the cell membrane. The transport function ensures the transfer of nutrients by the intercellular fluid. At the same time, waste material and substances that harm the body (allergens or salts of some heavy metals) are removed from the cells themselves.
- Synthesis of some complex proteins related to the hemostasis system (together with vitamin K). Thus, blood clotting, wound regeneration is accelerated, which prevents infection.
- Synthesis of neurotransmitters. These are the so-called conductors of biochemical signals related to the nervous system. The benefits of neurotransmitters are that they improve the quality of sleep and increase stress resistance.
- Normalization of the functioning of the endocrine system. The element is involved in the synthesis of hormones that help digest food. Calcium is also responsible for lipid metabolism, maintains the optimal concentration of glucose in the blood. The beneficial property of the mineral is considered to be the effect on fertility and metabolism.

Strong bones and osteoporosis prevention
With an insufficient intake of calcium, as well as endocrine disorders associated with menopause, the mineral is washed out from the bone tissue. Gradually, bones lose the necessary strong structure, which increases the risk of fractures. The most dangerous and harmful complication is a hip fracture.
Eating foods rich in calcium and dietary supplements allows you to maintain the required amount of the beneficial mineral. It is especially important to monitor the level of the substance for women of climacteric age.

Reduces the risk of kidney stones
Research has shown that dairy products aren't the only ones that help reduce kidney stones. Sufficient calcium intake is a way to prevent pathology. People who eat foods rich in minerals reduce the likelihood of developing kidney stones by about 20%.
Reduces PMS symptoms
This beneficial property is due to the ability of the substance to affect the functioning of the endocrine system. In addition, calcium affects the synthesis of neurotransmitters, the level of which affects psychoemotional disorders.
Regulates blood pressure
The element is useful for the elderly by reducing blood pressure. It has been found that in people suffering from hypertension, the level of calcium is often low in blood plasma.

Reduces the risk of cancer
Adequate intake of the mineral is especially beneficial for women with high cholesterol levels. Consumption of dairy products containing calcium on a regular basis is the prevention of malignant tumors of the digestive system.
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels are mainly found in old age and are associated with dysfunction of various organs and systems. In women in the climacteric period, there is a cessation of the synthesis of estrogens, which regulate not only the work of the cardiovascular system, but also the absorption of calcium.
Osteoporosis and pathology of the heart and blood vessels are often interconnected. With osteoporosis, there is a calcification of blood vessels, as well as heart valves. Thus, the mineral is washed out of the bones, but is deposited in the vessels, which is harmful.The use of foods containing calcium, supplements with minerals are beneficial in preventing dangerous pathologies.
Helps to lose weight
The element has a useful property, which is to block the absorption of fats in the gastrointestinal tract. The acceleration of metabolism, which is noted at normal concentration of the substance, also has a benefit.
Protects teeth
The benefits of calcium for teeth are beyond question. It is a basic building block in helping maintain a healthy smile. With a lack of a trace element, tooth decay and the development of gum disease are noted.
Regular intake of the mineral in the optimal amount is beneficial in the form of maintaining the hardness of the teeth. Calcium is useful for the enamel repair process that begins at the time of teething.

Normalizes acid-base balance
The trace element helps to maintain an optimal acid-base balance. Various diseases are usually the result of acidification, which is harmful. Cells cannot receive oxygen and nutrients in the required amount. Energy production is reduced. Thus, cell damage and insufficient repair is observed. The accumulation of acids leads to increased fatigue, excess weight and susceptibility to various diseases.
Reduces the risk of developing chronic diseases
Inadequate intake of the nutrient can harm in the form of the development of chronic diseases, for example, hypertension, osteoporosis. Regular intake of the mineral reduces the risk of various pathologies.
Why calcium is useful for children and pregnant women
The benefits of calcium for the body of a pregnant woman are due to the growth of the embryo and fetus. The trace element ensures the adequate development of the tissues of the unborn child, in particular, the skeleton, tooth rudiments. In addition, the mineral prevents the occurrence of preeclampsia in pregnant women.
Calcium is beneficial for a growing child's body due to its basic properties. Calcium deficiency in the body can provoke rickets, late teething and dental disease.

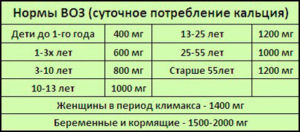
Daily intake
The benefits of the microelement are ensured through its use in the optimal dosage, which depends not only on age, but also on gender:
- 0-6 months - 400 mg;
- 6-12 months - 0.5 g;
- 1-5 years old - 600 mg;
- 6-10 years old - 800 mg;
- 10-13 years old - 1 g;
- 14-24 years old - 1.5 g;
- 25-55 years (women, men) - 1 g;
- from 55 years old (women) - 1500 mg;
- from 65 years old (men) - 1.5 g.
The dosage of the trace element is subject to adjustment during intense physical exertion, long-term therapy with hormones, anabolic steroids, glucocorticosteroid drugs. The dose of the element during pregnancy is increased to 2500 mg.
Signs of a lack of calcium in the body
There are several main reasons for calcium deficiency:
- unbalanced diet or diet;
- low levels of nutrients in the water;
- passion for coffee;
- smoking;
- intestinal candidiasis, enterocolitis, dysbiosis;
- pathology of the kidneys, pancreas and thyroid glands, hematopoietic organs;
- osteoporosis;
- estrogen deficiency;
- lack of digestibility of lactose;
- rickets;
- an excess of magnesium, zinc, potassium, phosphorus, which promotes the excretion of the nutrient;
- deficiency of D3;
- the period of pregnancy, accelerated growth, lactation, menopause;
- elderly age;
- intense mental and physical stress;
- using diuretics or laxatives.
A decrease in the concentration of a nutrient is harmful, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- weakness, decreased performance, fatigue;
- irritability and nervousness;
- head sweating;
- dry skin;
- tooth decay;
- cramps in the limbs;
- numbness of the fingers;
- Frequent fractures in bones, fractures indicating osteoporosis;
- tachycardia and other cardiac disorders;
- increased bleeding and poor blood clotting;
- increased sensitivity to cold;
- frequent infections, decreased immunity.
Symptoms of an excess of calcium in the body
If calcium in the body is elevated, they talk about hypercalcemia. This condition is not beneficial, but significant harm. Hypercalcemia often develops with excessive consumption of dairy products and Ca-rich water. Hypercalcemia is also common in older individuals.

The reasons for the excess of Ca:
- increased production of parathyroid hormone;
- malignant tumors of the lungs and kidneys;
- taking certain medications;
- hereditary pathologies;
- hormonal disorders.
Hypercalcemia may be asymptomatic. However, due to the properties of the trace element, the following symptoms sometimes occur:
- constant thirst;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea or vomiting;
- weakness, fatigue;
- constipation;
- loss of consciousness;
- convulsions at night;
- urolithiasis disease.
The harm of hypercalcemia is manifested by complications:
- hypertensionmanifested by high blood pressure;
- calcificationdenoting the deposition of Ca in tissues;
- hyperparathyroidism, accompanied by hyperfunction of the glands (parathyroid) and impaired salt balance.
The harm manifests itself in the development of angina pectoris and bradycardia, gastritis, ulcers.
Pharmacy preparations containing calcium
Pharmaceutical agents are intended for the treatment and prevention of pathological conditions and diseases that are caused by hypocalcemia and cause harm. Drugs are also prescribed to speed up the healing of various fractures.

The features of receiving funds include:
- the presence of the specified amount of a pure trace element;
- application simultaneously with food;
- exclusion of joint intake with carbonated drinks and coffee, anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant and laxatives, antibiotics (tetracyclines);
- consideration of contraindications (urolithiasis) and side effects, such as constipation.
Pharmaceuticals can be roughly divided into several groups:
- monopreparations (calcium carbonate, citrate, gluconate, lactate);
- combined preparations (calcium and vitamin D, other components);
- multivitamins (content of several vitamins and minerals to prevent hypocalcemia).
The most popular drugs include:
- Calcium D3 Nycomed;
- Vitrumcalcium with D3;
- Natekal D3;
- Complivit Calcium;
- Nature Bounty;
- KalceminAdvance;
- Marine calcium.
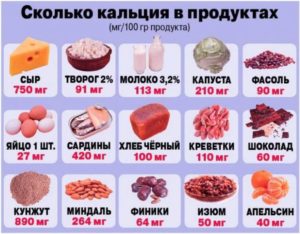
Calcium foods
Adequate nutrition is considered the best way to prevent hypocalcemia and other nutritional deficiencies. The trace element is found in various foods:
- vegetables;
- nuts;
- seafood;
- milk products.
The absorption of a nutrient from dairy products decreases with age. For example, the assimilation of an element from milk is 30%. Magnesium, vitamins C and D contribute to the absorption of Ca. The trace element is washed out of the bones due to:
- nicotine;
- carbonated products;
- sausages and smoked meats;
- salt.
Calcium harm to the body
The nutrient can be harmful if consumed in excess, due to its basic properties. Harm from taking can be expected with the simultaneous use of iron, magnesium, zinc. Scientists believe that the harm of Ca is manifested by an increased risk of malignant tumors of the prostate gland, heart disease with an excess of the trace element.

Calcium Compatibility with Other Substances
The benefits of the application can be expected only if the rules of admission are observed, which is associated with the properties of the trace element. It is known that the nutrient can react with other beneficial components. This affects the properties of calcium metabolism.
Vitamins belonging to the B group are combined with the nutrient. For example, vitamin B12 is not absorbed without calcium. Vitamin B6 slows down the excretion of a useful trace element. However, calcium blocks the absorption of zinc, iron and manganese. Thus, the interval between doses of these components should be 6 hours. Significant amounts of magnesium interfere with calcium absorption.
Conclusion
The benefits and harms of calcium have been studied extensively. Calcium is an essential chemical in maintaining body functions. The nutrient is useful if the optimal dosage is observed.

