Content
Vitamin B12 deficiency is common. Avitaminosis is more common among older people, as well as vegetarians who do not eat animal products. Lack of vitamin B12 leads to serious consequences for the body, which indicates the need for timely detection of pathology.
Causes of vitamin B12 deficiency
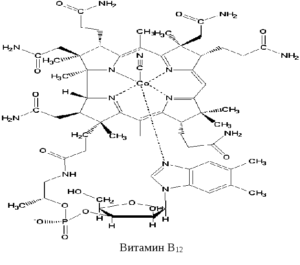
Cobalamin, known as vitamin B12, is a fat-soluble ingredient. The element is involved in the production of DNA and red blood cells. Influence on the adequate functioning of the nervous system is essential.
Often, the following categories of people lack vitamin B12:
- Elderly men and women. It is known that with aging, the mechanism of processing this component in the body is disrupted.
- Raw foodists, vegans and vegans. You should know that vitamin B12 is found in sufficient quantities only in animal products.
- Pregnant women. The increased need for a component is associated with the need to provide them with a growing organism.
- Violation of the mechanism of assimilation of cobalamin. Pathology occurs in celiac disease and Crohn's disease, resection of parts of the intestine.
- Taking some medications. With a decrease in blood glucose levels with Metformin, insufficient absorption of cobalamin is often noted.
Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency in adults
Vitamin B12 deficiency is accompanied by certain symptoms. If these signs occur, you should consult a doctor to rule out vitamin deficiency.
Symptoms of a lack of vitamin B12 in the human body include:
- Pallor of the skin and its yellowish tint... Usually, yellowness is noticeable on the cornea of the eyes. The characteristic skin tone occurs due to a decrease in the production of red blood cells, which are responsible for the pink color of the skin. DNA molecules, which are influenced by cobalamin, are responsible for the synthesis of red blood cells. Deficiency of vitamin B12 causes a type of anemia, implying the formation of so-called non-functional blood cells of significant size. They are unable to leave the bone marrow and enter the bloodstream. Non-functional cells are easily destroyed, provoking an increase in the concentration of bilirubin (the substance is produced by the liver during the utilization of erythrocytes). Bilirubin stains the cornea of the eye yellow.
- Increased fatigue and weakness... The symptom of a lack of vitamin B12 is a consequence of anemia. In this condition, there is a violation of the production of red blood cells responsible for the transport of oxygen to the tissues. It is known to be involved in obtaining energy from food. Lack of oxygen causes weakness and lethargy.
- Tingling in the limbs. A symptom of a lack of vitamin B12 is associated with damage to nerve cells and destruction of their membranes (myelin). Quite often parasthesias accompany anemia.
- Impaired coordination... Usually, a consequence of a lack of vitamin B12 occurs with untimely treatment of vitamin deficiency. The risk of poor coordination is associated with an increased risk of falls and serious injury. The symptom of vitamin B12 deficiency should be considered in older people due to osteoporosis. Falling often results in a hip fracture.
- Oral cancer, inflammation of the tongue... Glossitis is accompanied by soreness, changes in the shape and color of tissues. The tongue takes on a red tint. The surface is smooth due to the disappearance of the bumps containing taste buds.
- Dizziness, shortness of breath... These signs are due to anemia. If the transport function of blood is impaired, the body drives a larger volume of air through the lungs, which is manifested by an increase in the respiratory rate. However, these symptoms also indicate a number of other possible pathologies.
- Decreased visual acuity... Cobalamin deficiency leads to damage to the optic nerve. Thanks to it, signals are sent from the retina to the brain. Timely intake of cobalamin prevents optic neuropathy.
- Depression, dementia... With a decrease in cobalamin levels, the concentration of the amino acid homocysteine increases. The pathological process causes damage to the brain and a violation of the propagation of nerve impulses.
- Elevated temperature... The symptom is quite rare and has no scientific basis.
How to identify vitamin B12 deficiency
Experts point to certain difficulties in identifying vitamin deficiency. This is due to the appearance of signs of vitamin deficiency a few years after its development. Diagnostic difficulties are also due to the absence of specific deficiency symptoms.
Performing only a blood test to determine the concentration of vitamin B12 does not allow to unambiguously diagnose vitamin deficiency. The specific type of deficit is essential.

The clinical picture of vitamin B9 and B12 deficiency is similar. Their concentrations in the body are interrelated. A fall in folate (B9) levels leads to a decrease in cobalamin concentration.
When diagnosing vitamin deficiency, the doctor evaluates the clinical manifestations and laboratory diagnostic data. It is essential to exclude pathologies with similar symptoms. In some cases, consultation with an ophthalmologist, psychotherapist and other specialists is required.
What diseases are caused by a lack of vitamin B12
Cobalamin has a number of important functions in the body:
- Participation in the production of red blood cells (erythrocytes). Thanks to blood components, oxygen is transported to tissues, for example, organs, muscles. The level of hemoglobin directly depends on the concentration of red blood cells. Vitamin B12 deficiency often leads to anemia, symptoms of which are dizziness, muscle weakness, and constant fatigue.
- Ensuring adequate development of the fetus during pregnancy (its brain, as well as the nervous system). Vitamin deficiency is dangerous by the development of fetal abnormalities, miscarriage.
- Prevention of chronic fatigue, participation in metabolic processes. Cobalamin helps in the conversion of fats, proteins and carbohydrates into energy. Vitamin B12 deficiency causes muscle weakness and persistent fatigue.
- Maintaining an adequate state of the nervous system and brain health. Thanks to cobalamin, the protective sheaths of nerve cells are formed. A deficiency of the component leads to damage to the membranes, which is dangerous by impaired brain function. Thus, dementia, impaired coordination develop, and memory impairment progresses when the vitamin level approaches the lower limit. These consequences are associated with atrophy of the cellular elements of the brain.
- Normalization of the psycho-emotional state. Deficiency of cobalamin provokes the development of depression.This is due to the influence of the component on the production of the hormone serotonin, which is responsible for the regulation of emotions. Lack of vitamin B12 increases the risk of depression by 2 times.
- Benefits for vision. Cobalamin affects the nervous tissue. Visual information enters the brain via the optic nerve. Its damage, accompanied by loss of vision, is called optic neuropathy.
- Positive effect on the condition of bone tissue. Vitamin B12 deficiency leads to an increased risk of osteoporosis, according to research.
How to make up for the lack of vitamin B12
Cobalamin deficiency can lead to various disorders in the functioning of organs and systems. To eliminate vitamin deficiency, you need to include foods rich in vitamin B12 in the diet. In more severe cases, the doctor prescribes the intake of dietary supplements and medications.
Natural sources of B12
Cobalamin is found in the following animal products:
- fish (trout, salmon);
- meat and offal (liver, kidneys, beef, chicken);
- milk products;
- eggs.
Some foods are also fortified with vitamin B12:
- sports nutrition;
- bread;
- dry breakfasts;
- almond, rice, soy and other types of non-animal milk.
Dietary supplements and medicines
With a deficiency of vitamin B12, injections of cyanocobalamin or hydroxocobalamin are often prescribed. The use of these drugs is usually not accompanied by severe side effects. Allergic reactions sometimes occur.
As a result of scientific research, it has been proven that taking oral medications is as effective as injections. Vegans or vegetarians should take at least 10 mcg of cobalamin per day (or 2000 mcg once a week).
The most effective drugs for the treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency are represented by the following names:
- Methylcobalamin Thorne Research... The package contains 60 capsules. The medicine supports the health of the brain and nervous system, does not contain gluten. The dosage is 1-3 capsules per day.

- Sublingual Methylcobalamin Solgar... The drug is presented in an active coenzyme form. This dietary supplement is a kosher product that is also suitable for vegans. The capsules should be taken one per day. The total number of capsules in the package is 60 pieces.

- Fully Active B12 Doctor's Best... The benefits of a vegan product are scientifically proven. To increase the level of cobalamin, dietary supplements are taken 1 capsule per day. The package contains 60 capsules.

- Now Foods B-12... Lozenges (250 per pack) also contain folic acid. The product is suitable for vegans and vegetarians. According to the instructions, the dosage is 1 lozenge per day.

Prevention of vitamin B12 deficiency
Prevention of vitamin deficiency is the sufficient use of animal products. These include meat and offal, eggs, dairy products. You should also pay attention to those enriched with cobalamin: bread, breakfast cereals, sports nutrition.
To replenish vitamin B12 deficiency, you can take dietary supplements in oral form. Many experts point to the effectiveness of injections for the prevention of vitamin deficiency.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 deficiency is dangerous with serious health consequences at any age that are not always reversible. Signs of vitamin deficiency often appear after a long period of time. This indicates the need for adequate nutrition and preventive vitamin intake for people at risk.