Content
Among the components of various products, oxalates or oxalic acid salts are distinguished separately. These substances can aggressively affect body tissues. Products containing oxalates in significant quantities often provoke various pathologies. This indicates the need for careful planning of the diet.
What are "oxalates"
The term denotes acid (oxalic) salts. Substances enter the human body with some plant products. Their formation is also possible as a result of biochemical reactions.
Oxalates are characterized by a firm consistency and the presence of thorns (bumps) on the surface. The sharp edges of natural substances cause damage to surrounding tissues, their irritation, which leads to the appearance of pain.
An increase in oxalate levels increases the risk of kidney disease and the development of stone disease. Scientists suggest that high concentrations of oxalic acid salts provoke autism and damage to organelles (cell mitochondria). Their dysfunction provokes:
- fibromyalgia;
- pain;
- inflammatory processes;
- disorders in the functioning of the immune and nervous systems.
The following reasons are named that explain the excessive saturation of the body with oxalic acid salts:
- a genetic factor, consisting in the mutation of some genes;
- abuse of certain foods (citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, green vegetables);
- decreased activity of healthy intestinal microflora;
- hypervitaminosis C, B6 deficiency;
- violation of the transfer of oxalate ions through the membranes.
When are oxalates harmful?
Oxalic acid salts can have adverse effects on the body. Usually, a negative effect is observed with an excessive concentration of oxalates. Substances cause exacerbation of certain pathologies, for example, gout, rheumatoid arthritis.
What foods promote the formation of oxalates in the kidneys
Nutrition affects the production of oxalic acid salts. This is due to the composition of certain foods and their effect on the biochemical processes in the body. For example, ascorbic acid, found in citrus fruits, promotes the synthesis of oxalates. Vitamin B6, as well as magnesium and zinc, normalize the level of the substance in the body.
When compiling a diet, the concentration of oxalic acid salts should be taken into account. Depending on this indicator, the following product groups are distinguished:
- Low content - less than 2 mg (per serving). There is no need to limit products.
- The average content is 2-6 mg. You can consume no more than 3 servings of the specified food per day.
- High content - over 6 mg. This food is recommended to be excluded from the menu.
The tables show products containing varying amounts of oxalate.
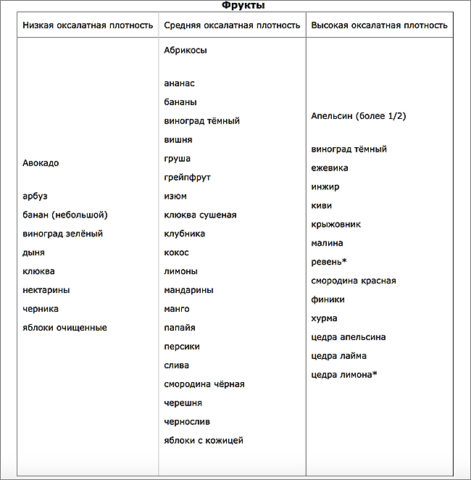
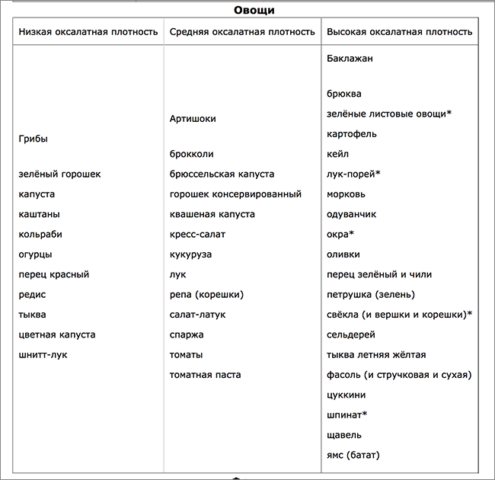
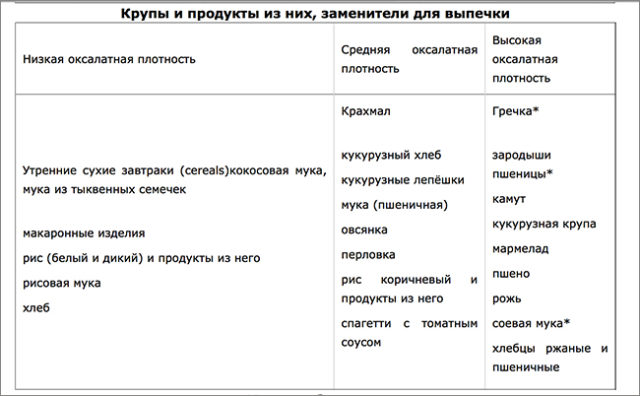
Oxalate content table in foods
The presence of oxalic acid salts in food is controversial. Food can be low, medium, or high. The table reflects information on the presence of oxalates in some foods:
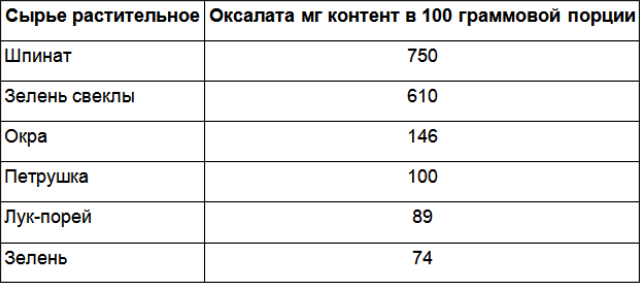
Foods high in oxalates
Products with a significant level of oxalic acid salts should be limited in use. Their exclusion is necessary in the presence of inflammatory processes in the body and diseases of the nephrological profile.
The following beverages are distinguished, which can cause excess substances:
- cocoa;
- beer;
- instant coffee);
- Black tea;
- rosehip broth.
The following vegetables and fruits have a high oxalate density:
- potatoes;
- parsley;
- pumpkin;
- celery;
- sorrel;
- spinach;
- zucchini;
- citrus fruits (orange, lemon, kiwi);
- blackberry;
- dark grapes;
- raspberry;
- Red Ribes;
- persimmon.
Legumes, nuts and cereals are rich in oxalic acid salts:
- lentils;
- beans;
- almond;
- cashew nuts;
- chia and sunflower seeds;
- soy;
- hazelnut;
- buckwheat;
- bran;
- wheat germ;
- corn grits.

Moderate oxalate content in food
Some names differ in the average value of the presence of oxalic acid salts:
- basil;
- yeast;
- ground pepper;
- cinnamon;
- Strawberry jam.
The list of products containing oxalates in small quantities includes dairy products, fish, cereals and legumes:
- yogurt;
- sardines;
- pearl barley;
- oatmeal;
- brown rice;
- peas;
- beans.
The average level of oxalates is determined in the following foods (fruits, vegetables, drinks):
- bananas;
- grenades;
- pears;
- grapefruit;
- Strawberry;
- tangerines;
- black currant;
- peaches;
- broccoli;
- corn;
- Brussels sprouts;
- onion;
- tomatoes;
- orange, cranberry, carrot, pomegranate juices.

Low oxalate foods
In case of kidney disease, this food group should be preferred. The following foods contain trace amounts of oxalates:
- ketchup;
- maple syrup;
- honey;
- gelatin;
- sugar;
- seaweed;
- spirulina;
- dill, garlic, horseradish, basil;
- vinegar;
- ginger.
Substances differ in low density:
- milk and kefir;
- fats and oils;
- meat (pork, lamb, poultry, beef);
- fish and seafood, eggs;
- breakfast cereals and semolina;
- fruits (watermelon, green grapes, melon, cherries, nectarines, mangoes, blueberries, apples);
- mushrooms;
- vegetables (cauliflower and white cabbage, Peking cabbage, cucumbers, radishes);
- coconut milk, cherry, grapefruit, apple juices.

What foods should be excluded with oxalates in the kidneys
Natural substances are synthesized in the human body (thanks to ascorbic acid), and also penetrate along with food. Their presence is possible due to the vital activity of intestinal bacteria.
Usually, oxalic acid salts are absorbed from foods in small quantities. However, the nature of the absorption depends on the state of the intestine. Excessive intake is associated with the following factors:
- inflammation of the digestive tract;
- steatorrhea (insufficient digestion of fats);
- the state of "leaky gut";
- chronic constipation.
To avoid exacerbation of diseases of the urinary system, you need to follow a diet. The diet involves limiting oxalate-containing foods that should not be consumed often:
- strong tea or instant coffee;
- citrus;
- rosehip broth;
- potatoes;
- sunflower seeds;
- Red Ribes.
Reducing the release of oxalic acid allows a restrictive diet with the rejection of the following names:
- offal (kidney, liver);
- salty fish;
- jelly;
- broths;
- canned tomatoes.
Conclusion
Knowing foods containing oxalates in large quantities is necessary for joint pathologies and diseases of the urinary system. Oxalic acid salts can contribute to pain, kidney stones, and exacerbation of disease.

